Download Amazon.com The Brink Of Bankruptcy Pdf
Overview: Amazon.com is one of a few examples of the dot com companies that managed to ride the wave of the dot.com bust, learning many lessons along the way; transforming them from being on the brink of bankruptcy and emerging as a success. Major Stakeholders Alternative Solutions Follow up Questions What are web based/internet companies (ie facebook, google) doing differently today than Amazon and other dot com business from the last decade?
Re- Program Your Subconscious Mind To Get What You Want. I’ve got an important question for you today. Do you have a fear of success? Even if you don’t think so. It has been more than a decade since the crash but from its ashes remains a select few companies who managed to hold on to their vision of internet domination.
How many have purchased products from Amazon.com within the last month? What did you learn that could apply to your industy? Solution Major Case Theme Conflicting business models: Profits versus Customers Major Stakeholders.Jeff Bezos (President & CEO).Amazon.com's Board of Directors, corporate executives, employees, customers, and the shareholders.Amazon.com’s SCM / VC and their employees. Amazon.com: The Brink of Bankruptcy Symptoms Amazon.com posted year over year financial losses Pressure from investors/shareholders to become profitable Multiple market segments continued to lose money Problems Amazon.com unable to react quickly to the rapidly changing economic environment Amazon.com operating expenses continue to increase greater than gross profits Early on, Amazon.com lacked the infrastructure to handle the volume of sales and distribution requirements to meet customer expectations. Bezo unable to articulate a clear business solution to mitigate the financial issues Opportunities High volumes of sales both in the US and International markets Potential for large market segments due to other dot com failures Evaluation Criteria for Success Decreased Operating Cost Dec. 1997 - ($31,020) Dec. 1999 ($719,968) Dec.
2000 -($1,411,273) Dec 2010 $0 Increased Stock Prices Dec. 1999 - $113.00 Dec. 2000 - $15.00 Dec. 2010 - $180.00 Increased year over year profits Dec. 1997 Income loss ($31,384) Dec.
2010 Income gain $1,406, 000 Path to Transformation Alternative Solutions Establish a financial plan Utilize IT to handle and decrease operational costs and expenses instead of increasing volume of sales. Allow IT to drive revenue growth (pg 108) Amazon.com could have utilize the IBM model H1, H2, H3 and taken the volme of sales data and focused on the market segments they were profitable and risk.
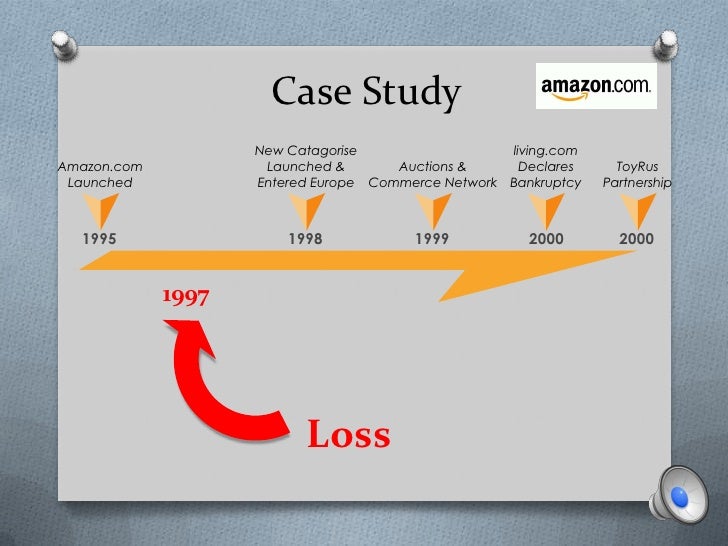
Solution Amazon.com realized that partnerships in the online toy industry were available and contracts made between Toys R US and Amazon.com. Timeline. 1994: Bezos, a N.Y. Investment banker with no book publishing or retail experience, identifies book retailing as an industry segment that could exploit the power of emerging internet technologies. Chooses Seattle as a location to be close to one of the largest book distributors. Writes the business plan and chooses the company name while driving cross-country with his wife.

1995: Between July 1994, when the company was incorporated and July 1995 when the amazon.com online bookstore was officially launched, Bezos and a few employees built the software that powered the web site. By September 1995, the company was selling over $20K per week out of the founder’s garage. 1996: Amazon.com focused on enhancing its product and service offerings and capabilities with increasingly sophisticated browsing and focused search capabilities, personalized store layout and recommendations, shopping carts, 1-Click shopping (which was alter patented).
1997: By the 1st quarter of 97, amazon.com revenues had increased to $16M (which was equivalent to the company’s yearly revenues in 1996). Amazon.com went public on 05/15/97. 1998: Beginning in 1998, amaonz.com began aggressively expanding into new product categories and into international markets. BY early 2001, the company was not just an online bookstore; it was an online superstore selling a wide variety of products in over 160 different countries. 1999” Amazon.com began exploring new business models including, auctions (low-end and high-end) and marketplaces (zshops). For these businesses, amazon.com provided software and services but did not assume control of inventory. As such, it acted as an agent – not a retailer.
2000: amazon.com expanded its marketplace business model through a series of equity partnerships with leading online retailers (drugstore.com, living.com, and pets.com). BY late 2000, living.com and pets.com had succumbed to the dot-0com crash and had declared bankruptcy.
This caused amazon.com execs to reevaluate the company’s business model. Rather than partner with dot-com retailers, attention shifted to traditional retailers that wished to develop online retailing capabilities and to upgrade their traditional distribution and fulfillment capabilities to enable the end-to-end visibility and speed required when doing business online. In August 2000, Amazon.com’s partnership with Toys R Us enabled the company to explore a new business model as a logistics services provider as it simultaneously expanded into a new market (traditional retailers) with its existing online retail product.
2004: Amazon.com posts it's first ever annal profit. (Corporate Information Strategy & Management).
When you place your first order on HBR.org and enter your credit card information and shipping address, 'Speed-Pay' ordering is enabled. 'Speed-Pay' is a service that saves the credit card details from your most recent purchase and allows you to re-use that card for future purchases. If you click the Speed-Pay button on any product detail page, your order will be charged to the most recent credit card information attached to your account and shipped (if applicable) to the last address we have on file for you. Ebook: A digital book provided in three formats (PDF, ePub, and Mobi) for the price of one. Accessible within “My Library” upon purchase.
States In The Brink Of Bankruptcy
Hardcopy, paperback, softbound, magazine: Physical copy shipped from our warehouse to your requested shipping location. PDF: PDF digital file. Accessible within “My Library” upon purchase. Bundle: A themed collection containing two or more items at a special savings. Note: Some of our products are available in other languages besides English, for example a “Spanish PDF” format means you will receive a PDF in the Spanish language. A security code is added protection against credit card fraud. It is a 3 or 4 digit number appearing on the front or back of your credit card.

See examples below. Visa and Mastercard The security code has 3 digits and appears on the BACK of the card in the signature panel. American Express The Card Identification Number (CID/4DBC) is a four-digit, non-embossed (flat) number that is printed on every American Express Card. The CID/4DBC is ALWAYS located ABOVE the embossed (raised) account number on the face of the card. In some instances, the CID/4DBC is located on the left side of the card, but is always above the account number. Some cards have a four-digit number embossed below the account number, but this is not the CID/4DBC.